SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT

STAKEHOLDERS

Information System Planning


SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT MODELS
• Waterfall Development
-Sequential process, structured design
•Rapid Application Development
– focuses on quick development
-Prototyping
– performs phases concurrently and repeatedly.
- Agile
- Extreme Programming
- Crystal, Scrum
WATERFALL MODEL
•Waterfall approach was the first SDLC Model to be used widely in Software Engineering to ensure success of the project.
•In "The Waterfall" approach, the whole process of software development is divided into separate phases.
•In Waterfall model, typically, the outcome of one phase acts as the input for the next phase sequentially.

A sequential software development model
Development is seen as flowing steadily downwards (like a waterfall) through the phases of requirements analysis, design, implementation, testing (validation), integration, and maintenance.

Waterfall Model Phases
Requirements analysis and definition
System and software design
Implementation and unit testing
Integration and system testing
Operation and maintenance
Advantages Of Waterfall Model
•Simple and easy to understand and use
•Easy to manage due to the rigidity of the model . each phase has specific deliverables and a review process.
•Phases are processed and completed one at a time.
•Works well for smaller projects where requirements are very well understood. •Clearly defined stages.
•Well understood milestones.
•Easy to arrange tasks.
•Process and results are well documented.
Disadvantages of the Waterfall Model
Difficulty of accommodating change after the process is underway.
One phase has to be complete before moving onto the next phase.
Inflexible partitioning of the project into distinct stages makes it difficult to respond to changing customer requirements.
Only appropriate when the requirements are well-understood and changes will be fairly limited during the design process.
Why NOT good for many projects
Real projects rarely follow the sequential flow that the model proposes.
Few business systems have stable requirements.
At the beginning of most projects there is often a great deal of uncertainty about requirements and goals, and it is therefore difficult for customers to identify these criteria on a detailed level. The model does not accommodate this natural uncertainty very well.
Assumptions made in the early phases may no longer hold
Some of the early work may be incomplete
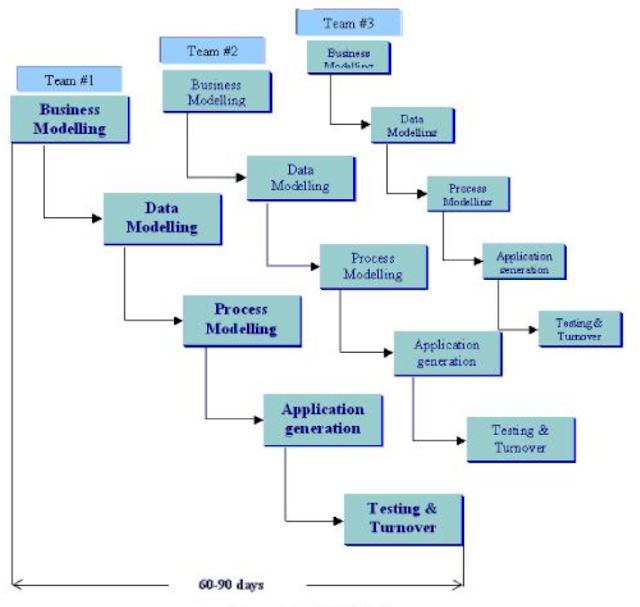
Rapid Application Development
An incremental software development process model that emphasizes an extremely short development cycle.
If requirements are well understood and project scope is constrained, the RAD process enables a development team to create a ‘fully functional system’ within very short time periods (eg. 60 to 90 days)
Involves
iterative development
construction of prototypes
use of Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) tools.
Traditionally this involves compromises in usability, features, and/or execution speed.
Why use RAD
to prevent cost overruns
to prevent runaway schedules
to converge early toward a design acceptable to the customer and feasible for the developers
to limit a project's exposure to the forces of change
to save development time, possibly at the expense of economy or product quality.
Advantages of Rapid Application Development
Increased speed of development
through methods including rapid prototyping, virtualization of system related routines, the use of CASE tools, and other techniques.
Increased end-user utility
Larger emphasis on simplicity and usability of GUI
Early visibility: because of prototyping
Greater flexibility: because developers can redesign almost at will
Greatly reduced manual coding: because of wizards, code generators, code reuse.
Increased user involvement: because they are represented on the team at all times
Possibly fewer defects: because CASE tools may generate much of the code
Possibly reduced cost: because time is money, also because of reuse
Shorter development cycles: because development tilts toward schedule and away from economy and quality
Standardized look and feel: because APIs and other reusable components give a consistent appearance.
Disadvantages of Rapid Application Development
Reduced Scalability, and reduced features when a RAD developed application starts as a prototype and evolves into a finished application
Cost of integrated toolset and hardware to run it
Reduced features occur due to time boxing when features are pushed to later versions in order to finish a release in a short amount of time.
Rapid Application Development Model
Agile methods
Dissatisfaction with the overheads involved in software design methods of the 1980s and 1990s led to the creation of agile methods. These methods:
Focus on the code rather than the design
Are based on an iterative approach to software development
Are intended to deliver working software quickly and evolve this quickly to meet changing requirements.
The aim of agile methods is to reduce overheads in the software process (e.g. by limiting documentation) and to be able to respond quickly to changing requirements without excessive rework.
Agile Software Development - Successes
Small or medium sized product development.
Custom system development within organization
Experiments in using agile approaches for critical systems engineering.
Security, safety, and dependability analysis
Need significant modifications before applying.
Drawbacks / Difficulties
Custom representatives are subject to other pressures and cannot take full part in the software development.
Individual team members may not have suitable personalities for the intense involvement / team work.
Prioritizing changes can be extremely difficult when there are lot of stakeholders.
Under pressure from delivery schedules, the team may not have time to carry system simplifications.
Cultural change – team members may find it hard to change the practice (informal / defined by team itself)






No comments:
Post a Comment